The transition to a circular economy requires rethinking the way we produce, consume, and manage resources. In this context, industrial symbiosis has become one of the most effective strategies for transforming waste, surpluses, and by-products into new value opportunities.
Far from being a theoretical concept, industrial symbiosis is an applied practice that allows companies and territories to improve their competitiveness, reduce environmental impacts, and generate new dynamics of collaboration, understanding it as an urban-agro-industrial symbiosis approach.
What is agro-industrial symbiosis?
Industrial symbiosis is a collaborative strategy between companies whereby the waste, by-products, energy, water, or services of one organization become resources for another.
The basic concept of industrial symbiosis is: The waste from one industry can be the resource of another.
This approach breaks with the traditional linear model (extract–produce–dispose) and promotes interconnected production systems, where the flows of materials and energy are jointly optimized. To do this, it is necessary to approach the industry with a systemic vision of the industrial environment and the management of its resources with an intersectoral approach. It is about considering industries as part of an industrial ecosystem, where surplus resources are exchanged, making efficient use of resources: the waste of one company can be the raw material of another.
Unlike conventional recycling, industrial symbiosis:
- Acts before the waste exists as such
- It is based on stable relationships between actors
- It generates economic, environmental, and strategic benefits simultaneously
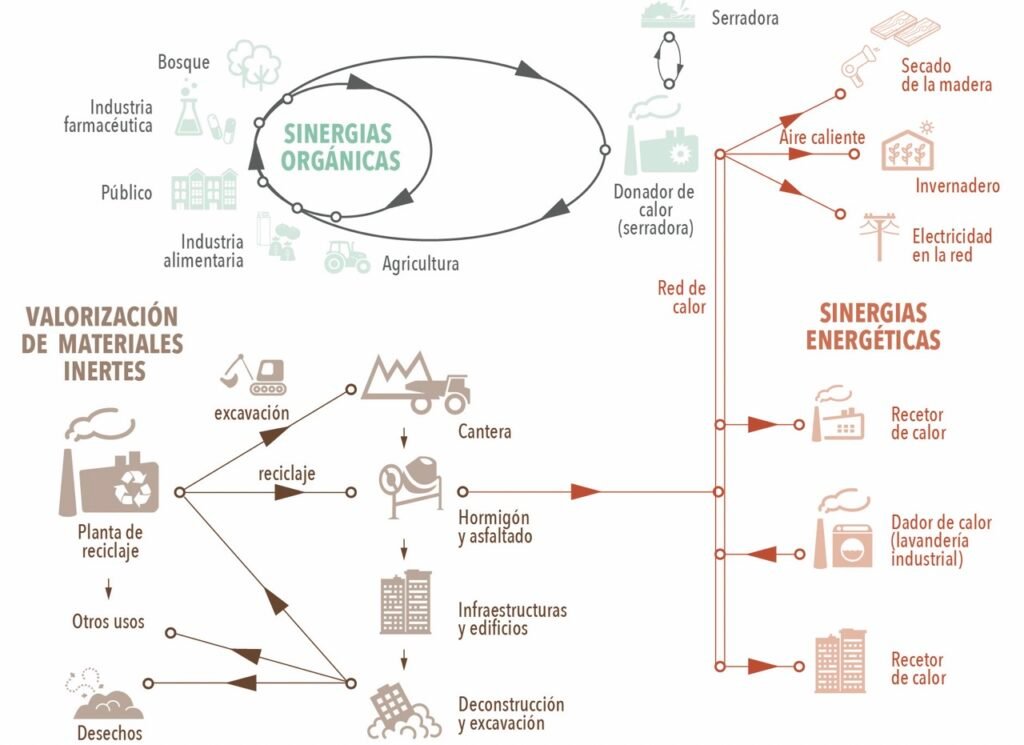
How does industrial symbiosis work?
An industrial symbiosis project is articulated from the identification and connection of different resource flows between organizations.
These exchanges can occur in different areas:
- Materials: by-products, recoverable waste, secondary raw materials
- Energy: residual heat, steam, surplus electricity
- Water: reuse of industrial or rainwater
- Infrastructure and services: logistics, storage, treatment
- Knowledge and capacities: innovation, technology, processes
The key is not only in the specific exchange, but in designing lasting collaborative systems, adapted to the industrial and territorial reality.
Benefits of industrial symbiosis
Environmental benefits
- Reduction of waste sent to landfill
- Decreased consumption of virgin raw materials
- Lower carbon and resource footprint
- More efficient use of energy and water
Economic benefits
- Reduction of waste management costs
- New sources of income from by-products
- Optimization of production processes
- Improvement of business competitiveness
Strategic benefits
- Regulatory compliance and exploitation of regulatory opportunities
- Greater resilience to supply crises
- Reinforcement of innovation and collaboration
- Improvement of corporate and territorial reputation
Examples of industrial symbiosis in practice
Industrial symbiosis is applied in very diverse sectors: agri-food, chemical, energy, metallurgical, construction, waste management, among others.
Some common examples include:
- Use of residual heat between nearby industries
- Valorization of industrial by-products as secondary raw materials
- Exchange of organic waste for biogas production
- Reuse of treated industrial water
- Shared use of infrastructure and logistics services
These examples demonstrate that the circular economy is not only an environmental objective, but a real lever for efficiency and development.
Industrial symbiosis in companies
For companies, industrial symbiosis represents an opportunity to:
- Reduce operating costs
- Optimize resource management
- Identify new business opportunities
- Advance their sustainability strategies
The key is to analyze internal flows, detect surpluses, and connect with other organizations that can take advantage of them in a viable and safe way. If you are a company, you can visit our page on how we work with companies to accompany them on their path towards sustainability.
Industrial symbiosis in territories and public administrations
In the territorial sphere, industrial symbiosis becomes a strategic tool for local development.
It allows administrations and public entities to:
- Boost the competitiveness of the productive fabric
- Justify public investments and attract European funding
- Promote more resilient economic models
- Coordinate local actors and generate projects with continuity
The territorial vision is key to scaling synergies and maximizing their economic, environmental, and social impact.
You can also visit our page on how we help administrations and territories to implement industrial symbiosis projects.
The role of the facilitator in industrial symbiosis
One of the critical success factors in industrial symbiosis projects is facilitation.
The facilitator:
- Analyzes and maps resource flows
- Identifies synergy opportunities
- Supports organizations in the design of solutions
- Coordinates the different actors involved
- Ensures technical, economic, and organizational viability
Without this figure, many opportunities remain unfulfilled due to lack of global vision, trust, or coordination capacity.
Industrial symbiosis: a real lever for the circular transition
Industrial symbiosis demonstrates that the circular economy is possible when combined:
- Technical knowledge
- Strategic vision
- Collaboration between actors
- Proven methodologies
Beyond a trend, it is a concrete tool to transform production systems, generate shared value, and move towards more sustainable and competitive models.
If you want to learn more about how industrial symbiosis projects are designed and implemented, you can explore the services, methodologies, and real cases developed by Simbiosy.

